

IB programmes are taught by teachers who explicitly help students learn how to develop the attitudes and skills they need for both academic and personal success.
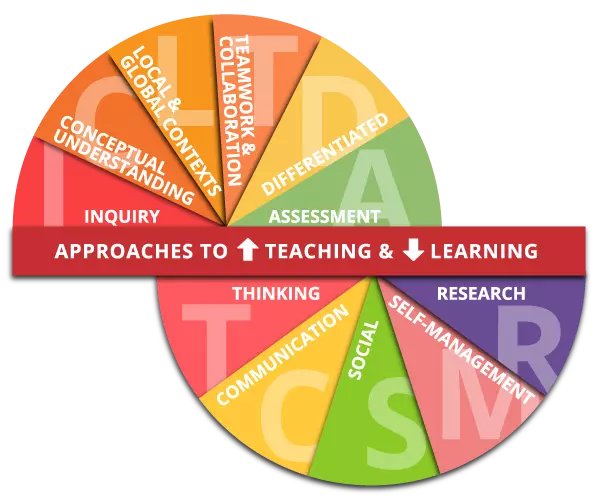
There are six key pedagogical principles that underpin all IB programmes. Teaching in IB programmes is:
This area develops essential skills that include skills of behaviour and emotional management, skills that allow the student to monitor their own effectiveness in their learning and skills that allow them to process information effectively (often called “study skills” in a school environment). Although these skills may be in use when developing a certain natural ability or talent, they are different from both ability and talent themselves because proficiency in any skill can be increased through the deliberate use of techniques and strategies, feedback and challenge. Skills are therefore highly teachable.
Teaching and learning in the all IB Programmes therefore incorporates the development of:
Although these are presented as distinct categories, there is some overlap and close connections between them. These categories should be seen as interrelated, as well as linking closely with the attributes highlighted in the IB learner profile. IB students work to become inquirers, knowledgeable, thinkers, communicators, principled, open-minded, caring, risk-takers, balanced and reflective.